Knives have been an essential tool and weapon for humans for centuries. They are used for various purposes such as hunting, self-defense, cooking, and more. Knives come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, and each type has a specific use. In this article, we will discuss the different types of knife weapons and their uses.
There are many different Types of Knife Weapons are among the most versatile and useful tools a person can possess. They come in many shapes and sizes, each with its own unique purpose. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the different types of knives weapons and their uses.
Combat Knives
Combat knives are specifically designed for military and self-defense purposes. They are built to withstand rugged use and are known for their durability and reliability in high-stress situations.
Characteristics of Combat knife

- Fixed Blade Design
Combat knives typically feature a fixed blade, meaning the blade is permanently attached to the handle without any folding mechanism. This design provides maximum strength and stability, making them suitable for heavy-duty tasks.
- Blade Shape and Length
Combat knives usually have a clip point or spear point blade shape. These blade profiles offer versatility for both piercing and slicing actions. The blade length can vary, but it is typically between 4 to 7 inches to strike a balance between maneuverability and effectiveness.
- Full Tang Construction
Combat knives often have a full tang construction, which means the blade extends the entire length of the handle, providing superior strength and durability. This design ensures the knife can withstand intense forces without breaking or separating.
- Ergonomic Handle
Combat knives are designed with ergonomics in mind to provide a secure and comfortable grip. Handles are commonly made from durable materials such as synthetic composites, rubber, or textured metals to ensure a firm hold even in wet or slippery conditions.
- Blade Material
Combat knives commonly use high-quality stainless steel or carbon steel for the blade. Stainless steel offers corrosion resistance and ease of maintenance, while carbon steel provides excellent strength and edge retention. Different blade coatings, such as black oxide or non-reflective finishes, are often applied to reduce glare and increase durability.
Additional Features: Some combat knives may include additional features to enhance their functionality, such as serrated edges for cutting tough materials like rope or webbing, sawback spines for notching or sawing, or pommel ends for use as an impact tool or glass breaker
Example types of Combat Knives
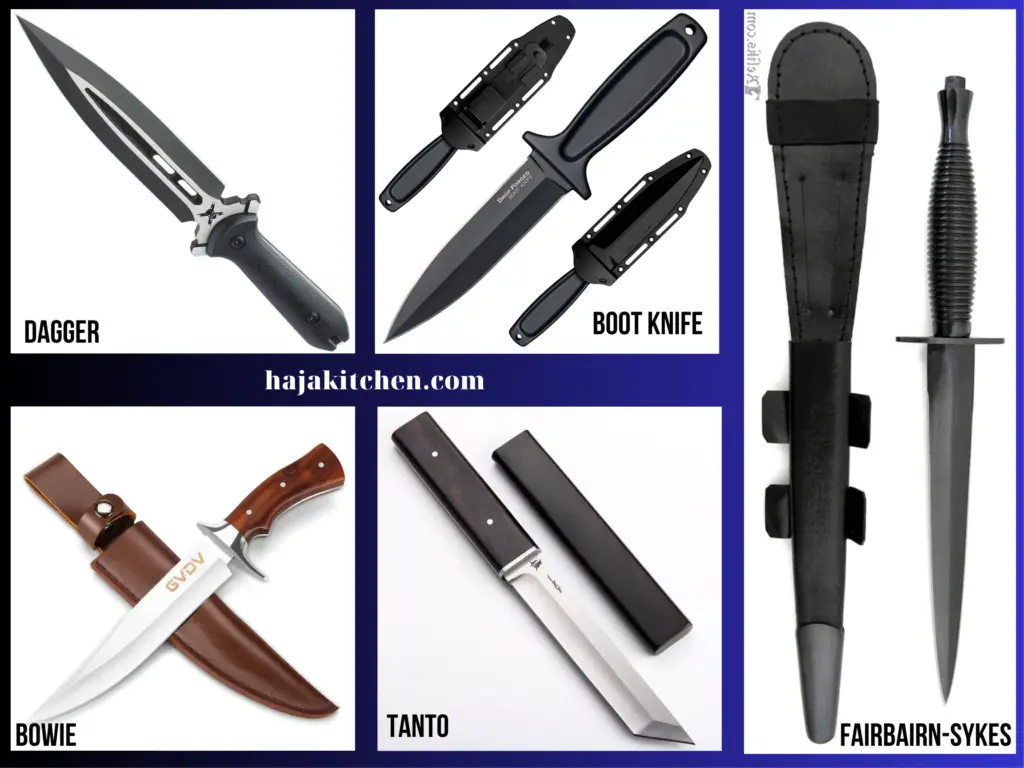

- Dagger: A double-edged knife with a symmetrical blade, primarily designed for thrusting and close-quarters combat.
- Bowie Knife: A large, fixed-blade knife with a clip point blade and a distinctive curved edge, originally designed for hunting but also used as a combat knife.
- Tanto Knife: Originating from Japan, the tanto knife features a straight edge and a reinforced tip, making it suitable for piercing and stabbing.
- Fairbairn-Sykes: A classic fighting knife with a double-edged blade and a slender profile, originally designed for British commandos during World War II.
- Boot Knife: Compact and lightweight, boot knives are designed to be easily concealed within or attached to a boot or shoe, providing a discreet and accessible self-defense option.
Tactical Knives
Similar to combat knives, tactical knives are versatile tools used by military, law enforcement, and outdoor enthusiasts. They often have folding blades for easy carry and deployment, and may feature additional tools or features. They are engineered to handle demanding situations and provide functionality in various environments.
Characteristics of Tactical Knives
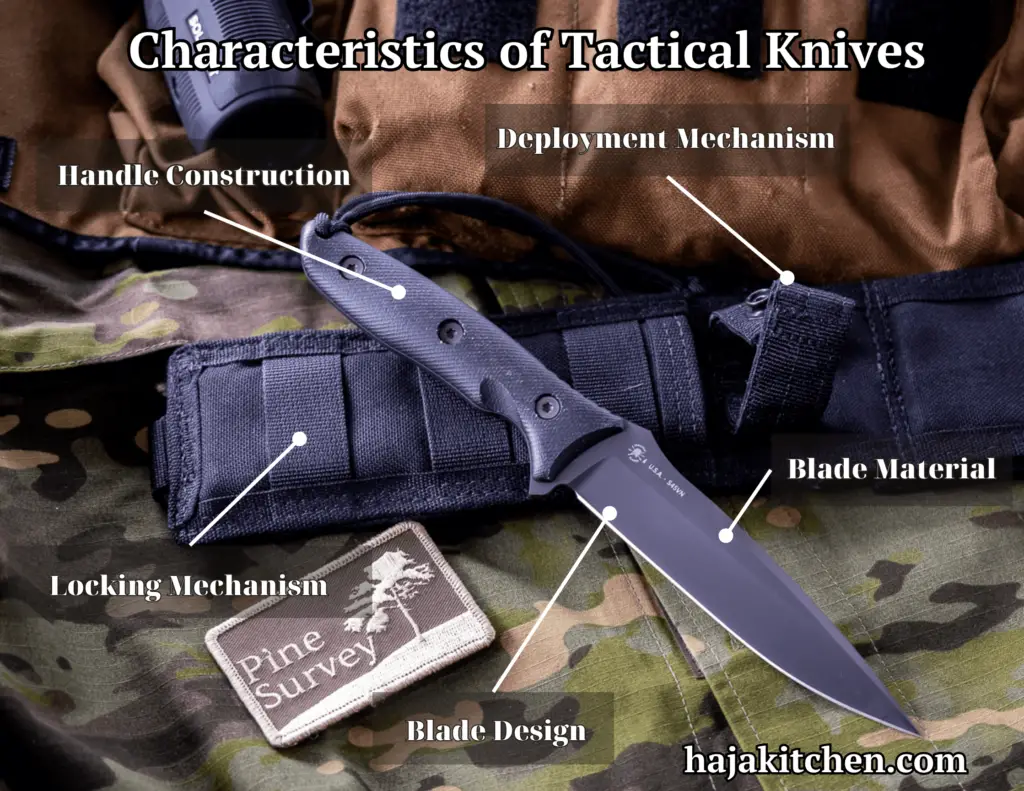
- Blade Design
Tactical knives often have a robust and durable blade design. They may feature a tanto, drop point, or spear point shape, which provides a strong tip and versatile cutting edge. Some tactical knives also have partially serrated blades to enhance cutting performance and versatility.
- Blade Material
High-quality blade materials are commonly used in tactical knives to ensure strength, sharpness, and corrosion resistance. Common blade materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and various types of tool steels such as S30V or D2 steel. The specific blade material depends on the intended use and desired characteristics of the knife.
- Handle Construction
Tactical knives typically have ergonomic and grippy handles to ensure a secure grip in challenging conditions. Handles may be made from materials such as G-10, micarta, or textured thermoplastic rubber to provide durability and a non-slip grip. Some tactical knives also feature handle designs with finger grooves or guard-like structures for added control and safety.
- Deployment Mechanism
Tactical knives often incorporate quick and reliable deployment mechanisms for easy and rapid one-handed opening. Common deployment mechanisms include thumb studs, flipper tabs, or assisted-opening mechanisms like spring-assisted or automatic opening systems.
- Locking Mechanism
Tactical knives commonly employ sturdy locking mechanisms to ensure blade security during use. Popular locking mechanisms include liner locks, frame locks, and lock-back mechanisms. These mechanisms provide a strong and reliable blade lockup to prevent accidental closure while the knife is in use.
Additional Features: Tactical knives may include additional features to enhance their functionality. Some examples include glass breakers, seatbelt cutters, integrated pommel for striking, or serrated edges for cutting through tough materials. These additional features cater to specific tactical or emergency situations.
Example types of Tactical Knives
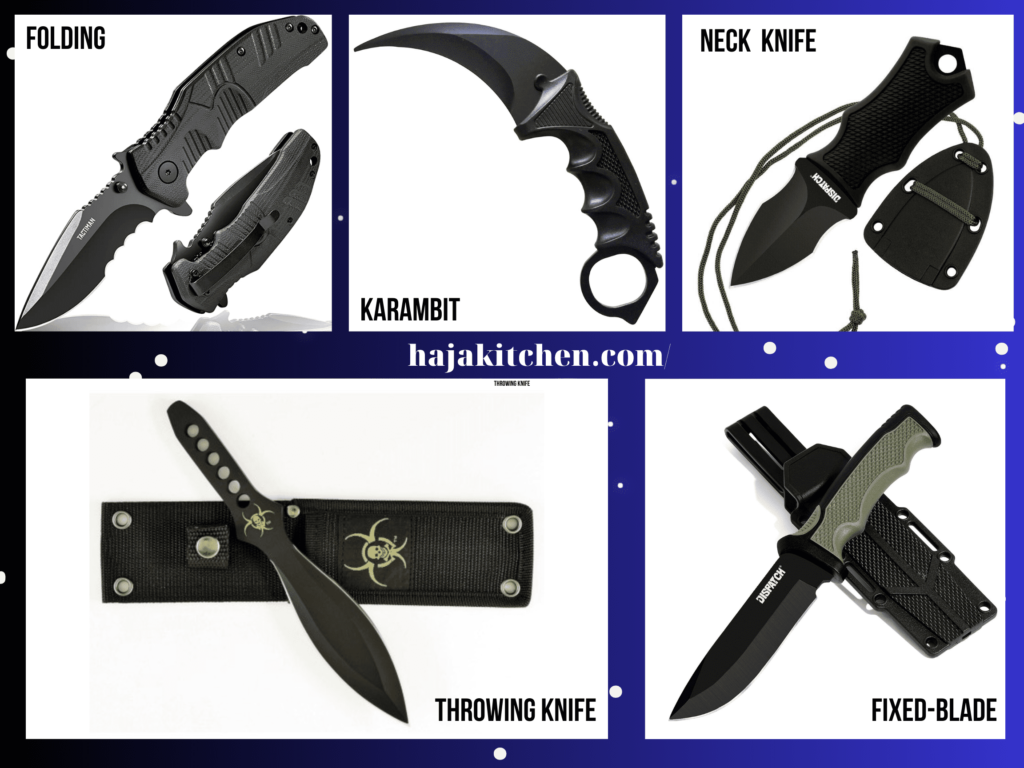

- Folding Tactical Knife: These knives feature a folding mechanism that allows for easy and compact storage. They often have assisted opening mechanisms, such as flipper tabs or thumb studs, for quick deployment.
- Fixed-Blade Tactical Knife: These knives have a solid, non-folding construction, providing maximum strength and durability. They are often preferred for heavy-duty tasks and survival situations.
- Neck Knife: Compact and lightweight, neck knives are worn around the neck on a cord or chain, offering quick access and concealment. They are often used as a backup weapon or for discrete self-defense purposes.
- Throwing Knife: Designed specifically for throwing, these knives have a balanced design and a sharp point, allowing for accurate and effective throwing techniques.
- Karambit: As mentioned earlier, karambit knives feature a curved blade and a finger ring. They are known for their slashing and hooking capabilities, making them suitable for tactical and self-defense purposes.
Fighting Knives
These knives are specifically designed for hand-to-hand combat and offensive purposes. They often have double-edged blades for thrusting and slashing, and may include features such as serrations or guards for added functionality.
Characteristics of Fighting Knives
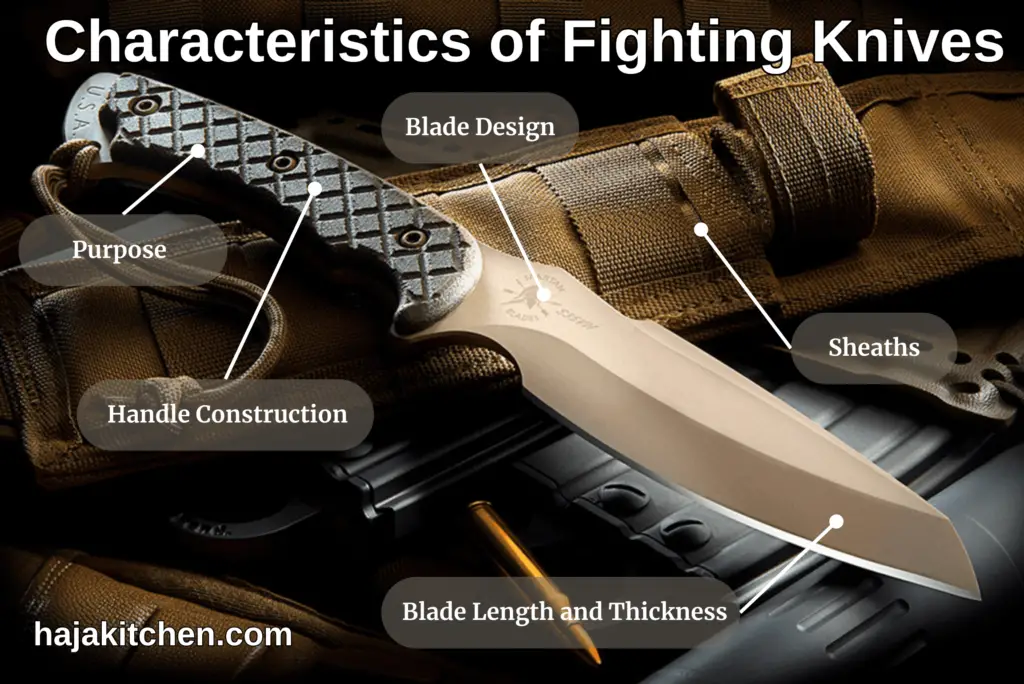
- Purpose
Fighting knives are primarily designed for close-quarters combat and self-defense situations. They are intended to inflict maximum damage with minimal effort and are typically used for stabbing, slashing, and thrusting motions.
- Blade Design
Fighting knives often feature specialized blade designs optimized for combat. Some common blade profiles include dagger-style blades, tanto blades, drop point blades, and clip point blades. These designs offer different advantages such as increased piercing power, strength, or versatility.
- Blade Length and Thickness
Fighting knives generally have medium to short blade lengths, typically ranging from 4 to 8 inches (10 to 20 cm). The blades are usually thicker and sturdier than those of everyday utility knives, allowing for greater strength and durability during combat situations.
- Handle Construction
The handles of fighting knives are designed to provide a secure grip, even in wet or slippery conditions. They may feature textured or contoured surfaces, ergonomic shapes, and materials that offer excellent grip and control, such as rubber, G10, or textured synthetic materials.
- Sheaths
A reliable sheath is essential for carrying and deploying a fighting knife quickly and safely. Sheaths for combat knives are typically designed for quick and easy access, with retention systems such as straps, snaps, or friction fit. Some sheaths may also feature multiple carrying options, such as belt loops, MOLLE attachments, or leg straps.
Military and Historical Significance
Fighting knives have played a significant role in military history, both as standard-issue equipment for armed forces and as iconic symbols. Many nations have developed their own specific fighting knife designs for their military personnel, often reflecting the unique needs and combat doctrines of each country.
Example types of Fighting Knives
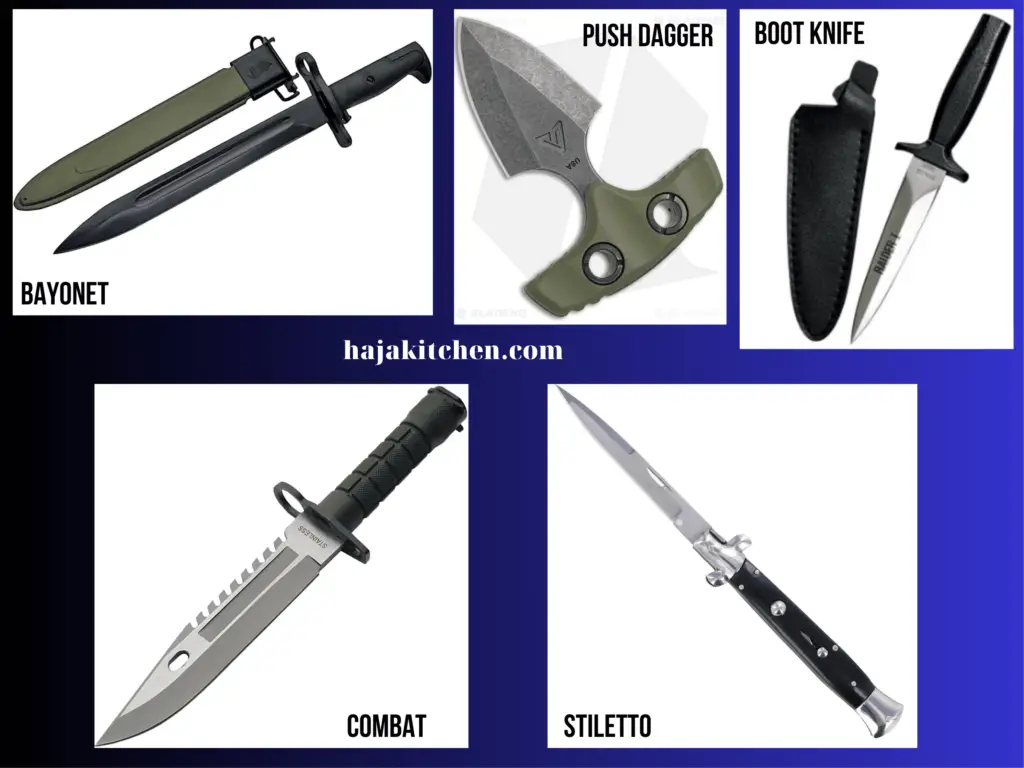

- Combat Knife: A general term referring to knives specifically designed for combat and military use. Combat knives can come in various shapes and sizes, but they are typically sturdy and versatile tools.
- Bayonet: A knife or blade attachment designed to fit on the end of a rifle or other firearm, effectively turning it into a spear-like weapon.
- Stiletto: A slender, dagger-like blade with a needle-like point, designed primarily for thrusting attacks.
- Push Dagger: Also known as a punch dagger or push knife, it features a short blade with a handle perpendicular to the blade, allowing for a powerful and controlled thrust.
- Boot Knife: A small, concealable knife designed to be carried in or attached to a boot, often used as a backup or last-resort weapon.
Throwing Knives
Throwing knives are a specialized type of knife designed specifically for throwing as a sport or for recreational purposes. Еhese knives have a balanced weight distribution and a sharp point. They require skill and practice to use effectively.
Characteristics of Throwing Knives

- Design
Throwing knives typically have a balanced design, with a symmetrical shape and weight distribution. This allows for consistent and predictable flight when thrown.
- Blade Shape
Throwing knives often feature a spear-point or double-edged blade design. The spear-point shape allows for better penetration upon impact, while double-edged blades offer versatility for rotational throwing techniques.
- Weight
Throwing knives are generally lighter than regular utility knives, weighing between 6 to 12 ounces (170 to 340 grams). The weight affects the knife’s stability and throwing distance.
- Blade Length
The blade length of throwing knives typically ranges from 6 to 12 inches (15 to 30 centimeters). Longer blades can provide more rotational stability during flight, while shorter blades offer better control and accuracy.
- Handle Design
Throwing knives usually have a straight or slightly curved handle without any protrusions or guard. The handle may have a textured or wrapped grip to enhance the thrower’s hold and prevent slippage.
- Material
Throwing knives are commonly made of stainless steel, carbon steel, or other durable materials that can withstand repeated throwing and impact without getting damaged.
Throwing Techniques
Throwing knives can be thrown using various techniques, including the no-spin, half-spin, or full-spin throws. Each technique requires different grip, stance, and throwing motion to achieve accuracy and distance.
Example types of Throwing Knives
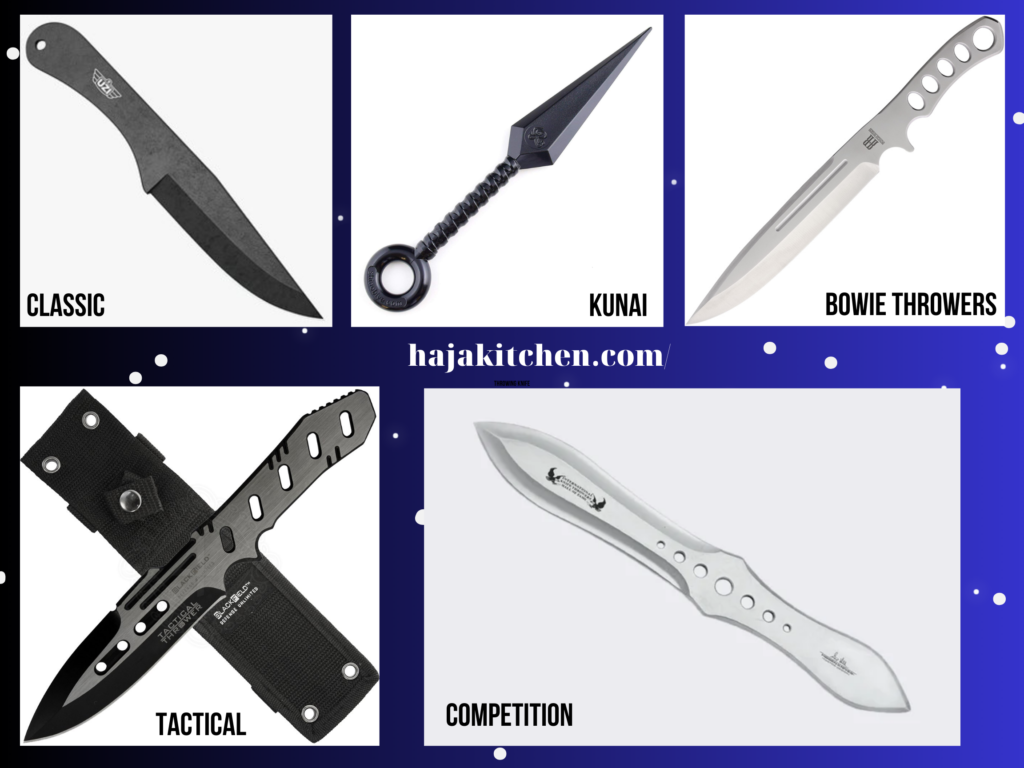

- Classic Throwing Knives: These are traditional throwing knives with a balanced design, often featuring a spear-point blade shape and a symmetrical handle. They are versatile and suitable for various throwing techniques.
- Kunai: Kunai knives have a long history in Japanese culture and are popular throwing knives. They typically have a straight blade with a tapered point and a ring or loop on the handle for attaching a rope or cord.
- Bowie Throwers: Inspired by the iconic Bowie knife, Bowie throwers feature a clip-point blade design with a pronounced belly and a sharp point. They offer excellent throwing stability and can be used for both throwing and utility purposes.
- Tactical Throwing Knives: These knives are designed with a tactical or military-inspired look. They often have a sleek and aggressive appearance, with features like black coating, serrations, or a combination edge. Tactical throwing knives are known for their durability and versatility.
- Competition Throwing Knives: These knives are specifically designed for competitive throwing events. They often have a standardized design with a particular weight and length to ensure fair competition. Competition throwing knives prioritize balance and accuracy.
Survival Knives
Survival knives are designed to help individuals survive in outdoor or wilderness environments. They often feature a sturdy fixed blade, a full tang construction, and additional survival tools like fire starters and whistle built into the handle.
Characteristics of Survival Knives
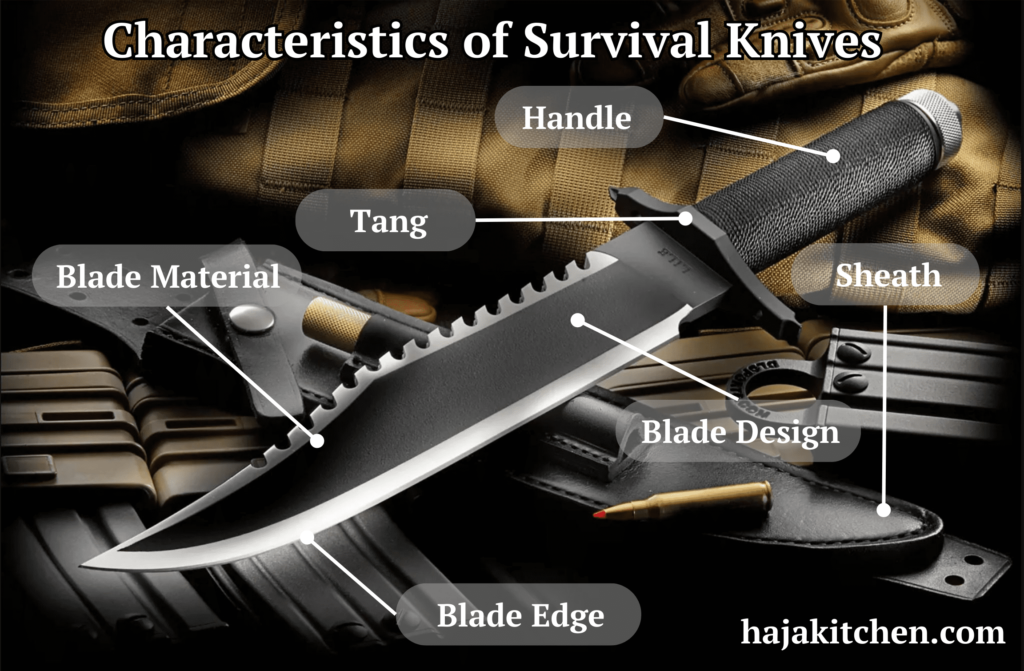
- Blade Design
Survival knives often feature a fixed blade design for strength and reliability. The blade length can vary, but it is typically between 4 to 6 inches (10 to 15 cm) for a balance between cutting ability and maneuverability. Common blade shapes include drop point, clip point, and tanto, each offering different advantages in terms of durability, piercing ability, and cutting versatility.
- Blade Material
High-quality blade materials are essential for survival knives to withstand tough conditions and retain sharpness. Common blade materials include stainless steel, carbon steel, and tool steel. Stainless steel is resistant to corrosion, while carbon steel offers excellent edge retention. Tool steel strikes a balance between the two, providing good toughness and edge retention.
- Tang
The tang refers to the portion of the blade that extends into the handle. Full tang knives have the blade extending the full length of the handle, providing strength and durability. Partial tang knives have a portion of the blade embedded in the handle, and while they are generally lighter, full tang knives are preferred for heavy-duty tasks.
- Handle
Survival knife handles should offer a secure and comfortable grip, even in wet or slippery conditions. Handles are commonly made from materials like rubber, G10, micarta, or synthetic composites. Some survival knives may feature textured or contoured handles for enhanced grip and ergonomic comfort.
- Blade Edge
Survival knives can have either a plain edge or a combination of plain and serrated edges. A plain edge allows for precision tasks such as carving, slicing, and food preparation. Serrated edges are effective for cutting through tough materials like rope or webbing. Some survival knives feature a partially serrated section near the handle for added versatility.
- Sheath
A reliable sheath is essential for safe storage and convenient carry of a survival knife. Sheaths are commonly made of leather, nylon, Kydex, or molded polymers. Look for a sheath with a secure retention system, belt loops or attachment options, and a protective design to prevent accidental injury.
Additional Features: Some survival knives may have additional features built into the design, such as a built-in firestarter, whistle, or compartment for storing small survival items. These extra features can add value and utility in emergency situations.
Example types of Survival Knives
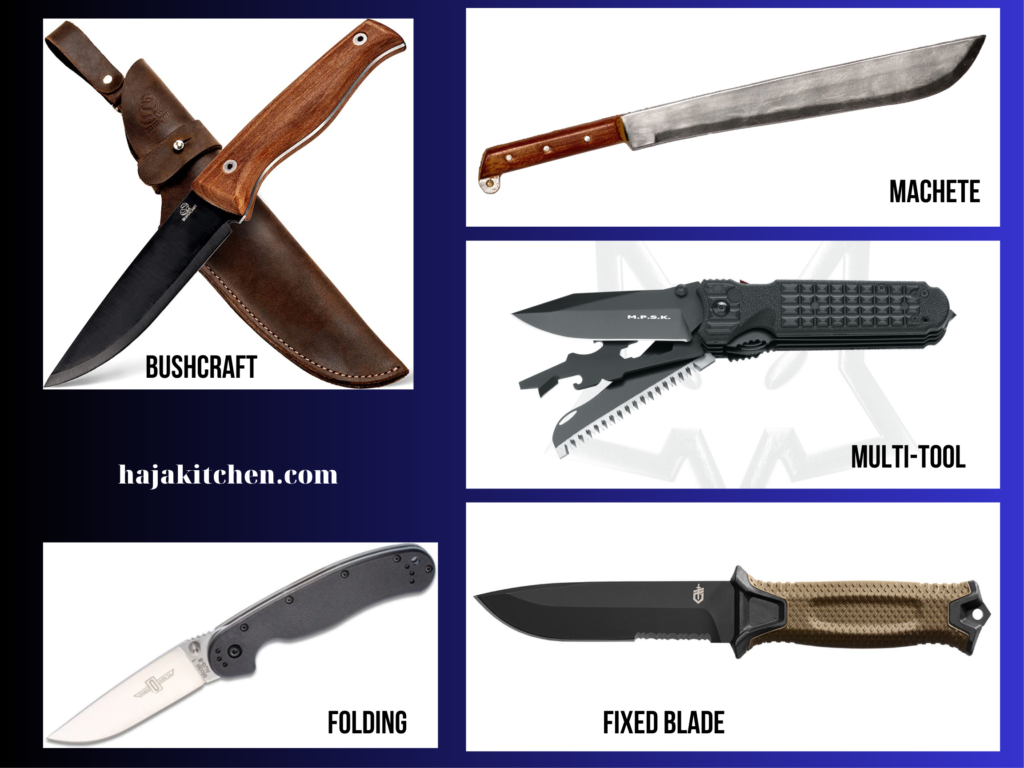

- Fixed Blade Survival Knives: These knives are the most common type of survival knife. They have a fixed blade that extends into the handle, providing strength and durability. Fixed blade survival knives are versatile and suitable for various tasks such as cutting, chopping, prying, and self-defense.
- Folding Survival Knives: Folding survival knives feature a hinged blade that can be folded into the handle for compact storage. They are portable and convenient for everyday carry. While folding knives may not be as robust as fixed blade knives, they offer versatility and are useful for lighter survival tasks.
- Bushcraft Knives: Bushcraft knives are specifically designed for wilderness survival and bushcraft activities. They typically have a medium-length blade with a flat or Scandi grind, allowing for precise carving, woodwork, and general outdoor tasks. Bushcraft knives often have a full tang construction for durability.
- Machetes: While not strictly a knife, machetes are popular tools for survival situations. They have a long, broad blade with a distinctive shape that excels at cutting through vegetation, clearing trails, and processing wood. Machetes are commonly used in tropical and jungle environments.
- Multi-tool Survival Knives: These knives incorporate additional tools and features into their design, such as pliers, screwdrivers, saws, can openers, and more. Multi-tool survival knives offer a range of utility functions in a compact package, making them ideal for various survival scenarios.
Utility Knives
Utility knives are multipurpose tools commonly used for everyday tasks such as cutting, slicing, and opening packages. They typically have a folding or retractable blade and can be carried easily.
Characteristics of Utility Knives
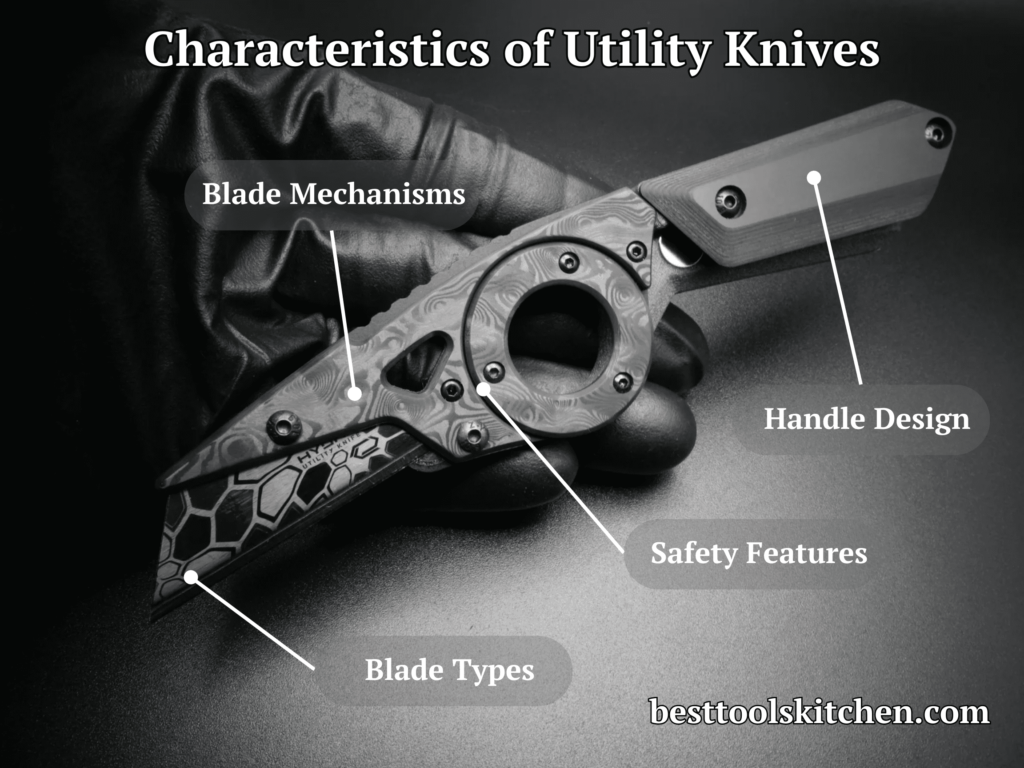
- Blade Types
Utility knives typically feature replaceable blades that come in different types and shapes. The most common blade type is the straight edge blade, which is ideal for general-purpose cutting. Other blade types include serrated blades for cutting through tough materials like rope or cardboard, hook blades for precision cutting and scoring, and specialty blades for specific applications such as scraping or deburring.
- Handle Design
Utility knife handles come in various designs to provide comfort, control, and durability. They are often made of materials like plastic, rubber, or metal. Some utility knives have ergonomic handles with contours or textured grips to enhance grip and prevent slippage during use. Additionally, some handles feature built-in storage compartments for extra blades, allowing for convenient and quick blade replacements.
- Blade Mechanisms
Utility knives employ different blade mechanisms to control the exposure and retraction of the blade. The most common mechanism is the retractable blade, which allows you to adjust the blade’s length and retract it into the handle for safe storage. Other mechanisms include folding blades that fold into the handle, fixed blades that remain exposed, and snap-off blades that can be segmented and snapped off when one section becomes dull.
- Safety Features
Many utility knives incorporate safety features to reduce the risk of accidents during use. Some knives have blade locks or mechanisms that keep the blade securely in place during cutting. Others feature automatic blade retraction systems that retract the blade into the handle once you release the handle’s pressure. There are also utility knives with retractable blade guards or shields that cover the blade when not in use, minimizing the risk of accidental cuts.
Applications
Utility knives find applications in various industries and activities. They are commonly used for tasks such as opening packages, cutting cardboard, trimming materials, slicing rope or tape, scoring surfaces, and performing light-duty cutting in construction, crafts, DIY projects, gardening, and more. Their compact size and versatility make them a handy tool to have in your toolbox, kitchen drawer, or utility belt.
Example types of Utility Knives

- Retractable Utility Knife: This is the most common type of utility knife, featuring a retractable blade mechanism that allows you to control the length of the exposed blade. It typically has a handle with a sliding mechanism that retracts the blade for safe storage.
- Fixed Blade Utility Knife: Unlike retractable utility knives, fixed blade utility knives have a non-retractable blade that remains exposed. They are sturdier and more durable, suitable for heavy-duty cutting tasks that require extra strength and stability.
- Snap-Off Blade Knife: Snap-off blade knives have segmented blades that can be easily snapped off when they become dull, revealing a fresh cutting edge. These knives are popular for applications that require frequent blade changes, such as arts and crafts, construction, and packaging.
- Folding Utility Knife: Folding utility knives have a hinged design that allows the blade to fold into the handle, providing compactness and portability. They are convenient for carrying in pockets or tool kits and often feature a locking mechanism to secure the blade in the open position.
- Hook Blade Utility Knife: Hook blade utility knives have a specialized curved blade with a hook-shaped tip. These knives are commonly used for cutting materials like carpet, vinyl, or linoleum. The hook design allows for precise cutting without damaging the underlying surface.
Spring-Assisted Knives
Spring-assisted knives, also known as assisted-opening knives, are a type of folding knife that utilize a spring mechanism to assist in the opening of the blade. They are designed to combine the convenience and quick deployment of an automatic knife with the legal and functional benefits of a manual folding knife.
Characteristics of Spring-Assisted Knives

- Opening Mechanism
The primary characteristic of spring-assisted knives is their opening mechanism. Unlike traditional manual folding knives that require full manual opening, spring-assisted knives use a spring-loaded mechanism to assist in blade deployment. This mechanism allows for quick and easy one-handed opening with minimal effort. Common opening mechanisms include thumb studs, flipper tabs, or thumb holes on the blade that can be easily accessed and engaged by the user.
- Spring System
The spring mechanism in spring-assisted knives plays a crucial role in their functionality. It assists in opening the blade swiftly and smoothly once the user initiates the opening action. The spring is typically located inside the handle and is activated by a manual action, such as pressing the thumb stud or using the flipper. The spring provides the necessary force to overcome the resistance of the blade and deploy it with speed.
- Versatility
Spring-assisted knives come in a wide range of designs and styles, making them versatile tools for various applications. They can be found in different blade shapes (e.g., tanto, drop point, clip point), handle materials (e.g., G-10, aluminum, stainless steel), and sizes to suit different needs and preferences.
- Manual Assistance
Despite the assistance provided by the spring mechanism, spring-assisted knives still require manual initiation of the opening process. The user needs to apply some pressure, typically through the thumb or index finger, to start the blade deployment. This manual assistance is a safety feature that prevents accidental opening and ensures the user maintains control over when and how the blade is deployed.
- Safety Features
Spring-assisted knives often incorporate safety features to prevent unintended blade deployment. Common safety mechanisms include liner locks, frame locks, or other locking mechanisms that secure the blade in the open position during use. These locks provide stability and ensure that the blade remains securely in place until intentionally closed.
Legal Considerations
The legal status of spring-assisted knives can vary depending on local laws and regulations. In many jurisdictions, they are considered legal for everyday carry since they are not classified as automatic knives. However, it’s important to be aware of any restrictions or specific regulations regarding blade length, opening mechanisms, or other features that may apply in your area. Always familiarize yourself with local knife laws to ensure compliance.
Example types of Spring-Assisted Knives
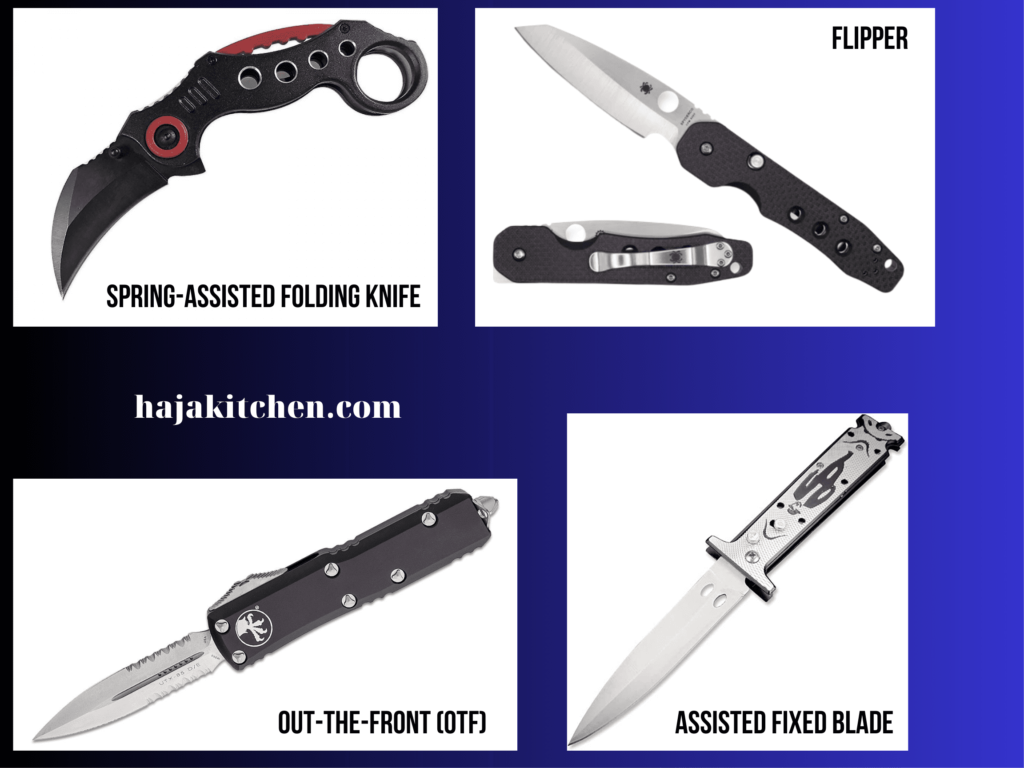

- Spring-Assisted Folding Knives: These are the most common type of spring-assisted knives. They have a folding design where the blade is stored inside the handle and can be deployed quickly with the assistance of a spring mechanism. The blade is typically activated by manually opening the knife partially, and then the spring takes over to fully deploy the blade into the open position.
- Flipper Knives: Flipper knives are a specific type of spring-assisted folding knife. They feature a protrusion or “flipper” on the back of the blade that can be easily accessed with the index finger. By applying pressure on the flipper, the blade rapidly deploys with the help of the spring mechanism. Flipper knives are known for their quick and smooth blade deployment.
- Out-The-Front (OTF) Knives: OTF knives, also known as automatic out-the-front knives, are spring-assisted knives where the blade is deployed straight out the front of the handle instead of swinging open like traditional folding knives. These knives have a sliding button or lever that activates the spring mechanism and extends the blade forward. OTF knives are often favored for their speed and ease of use.
- Assisted Fixed Blade Knives: While less common, there are also assisted-opening fixed blade knives available. These knives combine the benefits of a fixed blade (sturdiness and strength) with the convenience of assisted opening. The blade is typically housed in a sheath or holster and can be quickly deployed by activating the spring mechanism.
Conclusion
Top Knives and weapons are versatile tools and weapons that have been used by humans for centuries. They serve various purposes, including cutting, slicing, stabbing, self-defense, hunting, survival, and more. Different types of knives are designed for specific tasks and situations, each with its own features and characteristics.
It’s important to note that the use of different knives weapon types and specific knife types may be subject to legal restrictions in different jurisdictions. Always abide by local laws and regulations when using or carrying knives.
FaQ
What is a tactical knife used for?
A tactical knife is typically used for combat and self-defense situations. It can be used to cut through tough materials, open boxes, and perform other tasks that require a sharp and durable blade.
How is a tactical knife different from a regular knife?
A tactical knife is specifically designed for use in high-pressure situations like combat or self-defense. It typically has a serrated edge, a durable and ergonomic handle, and other features that make it more effective and reliable than a regular knife.
Is it legal to carry a tactical knife?
The legality of carrying a tactical knife varies depending on your location and local laws. It’s important to check your local laws and regulations before carrying a tactical knife in public.
How do I maintain my tactical knife?
To maintain your tactical knife, you should clean it regularly and keep it oiled to prevent rust and other forms of corrosion. You should also sharpen the blade regularly to ensure that it stays sharp and effective.
Can I use a tactical knife for everyday tasks?
While a tactical knife is designed for use in high-pressure situations, it can also be used for everyday tasks like opening boxes or cutting rope. However, it’s important to be mindful of the knife’s sharpness and to use it safely and responsibly.


